Hacking is easy. And profitable. An average phishing attack could potentially cost a mid-sized organization $1.6 million. Phishing is just one of the many ways that an organization can be attacked or breached.
Network security threats come in many different forms, but they all pose a serious threat to the safety and security of networked systems. While information security threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, there are a number of steps that organizations can take to protect their networks from these dangers
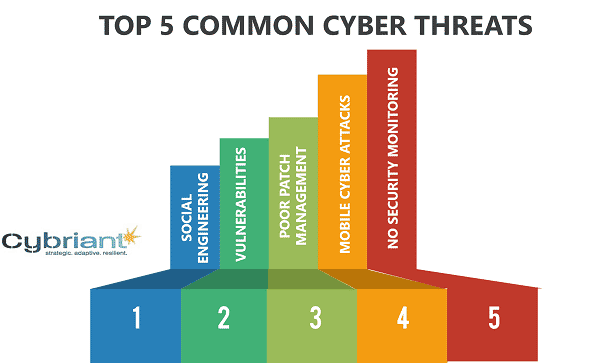
Let’s talk about the top 5 most common security threats.
Common Network Security Threats #1: Social Engineering
Social engineering, in the context of information security, refers to psychological manipulation of people into performing actions or divulging confidential information. Wikipedia
While we typically think of email as the main source of social engineering, hackers can gain your trust through phone, email, snail mail, or direct contact. The intention is to gain access to a system that would be too difficult for them to hack into.
Phishing or Spear phishing may be the top techniques used by social engineers to get your confidential information. Cybriant partner, KnowBe4, has compiled a list of top 10 techniques that the bad guys typically use. The list includes:
- Pretexting
- Phishing
- Water-holing
- Diversion theft
- Spear phishing
- Baiting
- Quid Pro Quo
- Tailgating
- Honeytrap
- Rogue
See the KnowBe4 article, “What is Social Engineering” for a more detailed look into those techniques.
Common Network Security Threats – Social Engineering Stats:
- 1 in 131 emails contains malware.
- 4,000+ ransomware attacks occur daily.
- The number of Phishing Attacks increased 65% last year.
- phishing attack costs a mid-sized company $1.6 million.
- 47% of attacks in 2017 caused by phishing.
Common Network Security Threats #2: Technical Vulnerabilities
A vulnerability is a weakness of an asset or control that could potentially be exploited by one or more threats. An asset is any tangible or intangible thing or characteristic that has value to an organization, a control is an administrative, managerial, technical, or legal method that can be used to modify or manage risk, and a threat is any potential event that could harm an organization or system. Source: ISO 27001
Many organizations confuse Vulnerability Management and Vulnerability Scanning. Performing only a single vulnerability scan each year or quarter puts organizations at risk of not uncovering new vulnerabilities. The time between each scan is all an attacker needs to compromise a network. With continuous scanning, our security experts automatically have visibility to assess where each asset is secure or exposed.
Today, security professionals find themselves chasing the “threat of the week,” often to no avail. Racing ahead without context and prioritization results in reactive firefighting and pursuit of the wrong issues. Performing the security basics well demands insight and focus.
Fortunately, vulnerability remediation doesn’t always have to be performed overnight, although the highest risk issues should be addressed quickly.
According to a comprehensive assessment of global data breach statistics, 99.9 percent of the exploited vulnerabilities were compromised more than a year after the common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE) was published.
In other words, if organizations would patch their vulnerabilities in less than a year, they could improve their chances of preventing an exploit-initiated data breach by as much as 99.9 percent.
Excerpt from “The Modern Approach to Vulnerability Scanning”
Common Network Security Threats – Technical Vulnerabilities Stats:
- More than 90% of exploited vulnerabilities in 2015 were more than one-year-old and nearly 20% were published more than 10 years ago.
- 8,000 vulnerabilities a year were disclosed over the past decade.
- 85% of successful hacks used the top 10 exploits.
Common Network Security Threats #3: Poor Patch Management
Patch management is a strategy for managing patches or upgrades for software applications and technologies. A patch management plan can help a business or organization handle these changes efficiently. Techopedia
A poor patch management plan can put a company at risk of hackers finding ways through their systems via vulnerabilities. [See Equifax]
A proper patch management plan will help your organization find missing security patches, support multiple systems and platforms, and handle increased compliance restraints. Related: The Financial Industry’s Biggest Threat
Common Network Security Threats – Poor Patch Management Stats:
- 45% of companies are not using a dedicated patch management solution to distribute and manage software updates.
- 72% of decision-makers do not deploy a patch within 24 hours after it is released to the public.
- Failure to patch caused the infamous Equifax breach, releasing the data of 143 million people.
Common Network Security Threats #4: Compromised Endpoints
Compromised endpoints are a common computer security threat that has become much more common in the mobile era that we live in today. BYOD means that employees are connecting their own devices to a corporate network. While this helps an employee’s productivity, it may cause problems for an organization’s network since corporate policy may not be enforced on the device.
This threat is very closely related to common network security threats – social engineering. That is because many compromised endpoints are caused by social engineering including phishing attacks that cause an end user to download malicious software onto their devices.
What is the risk of letting malware execute? Download our ebook: Prevention vs. Detect and Respond.
Common Network Security Threats Compromised Endpoints Stats:
- In Q1 of 2017 alone, mobile ransomware attacks increased by 253%.
- 66% of security professionals doubt their organizations can prevent a breach of employees’ devices.
- Most mobile attacks occur on businesses in the US. Businesses average 54 mobile malware infections.
Common Network Security Threats #5: Advanced Persistent Threats
An advanced persistent threat is a set of stealthy and continuous computer hacking processes, often orchestrated by a person or persons targeting a specific entity. An APT usually targets either private organizations, states or both for business or political motives. APT processes require a high degree of covertness over a long period of time.
The “advanced” process signifies sophisticated techniques using malware to exploit vulnerabilities in systems. The “persistent” process suggests that an external command and control system is continuously monitoring and extracting data from a specific target. The “threat” process indicates human involvement in orchestrating the attack.
APT usually refers to a group, such as a government, with both the capability and the intent to target, persistently and effectively, a specific entity. The term is commonly used to refer to cyber threats, in particular, that of Internet-enabled espionage using a variety of intelligence gathering techniques to access sensitive information,but applies equally to other threats such as that of traditional espionage or attacks.
Other recognized attack vectors include infected media, supply chain compromise, and social engineering. The purpose of these attacks is to place a custom malicious code on one or multiple computers for specific tasks and to remain undetected for the longest possible period. Knowing the attacker artifacts, such as file names, can help a professional make a network-wide search to gather all affected systems.[4] Individuals, such as an individual hacker, are not usually referred to as an APT, as they rarely have the resources to be both advanced and persistent even if they are intent on gaining access to, or attacking, a specific target. Wikipedia
Common Network Security Threats Advanced Persistent Threats Stats:
- 81% of data breach victims do not have a system in place to self-detect data breaches.
- Many companies rely on notifications from third parties to let them know about a data breach on their network, increasing the time to detection from 14.5 days to 154 days.
According to the FBI, business email compromise (BEC) alone cost businesses worldwide over $5 billion from 2013 to 2016.
Here’s the disconnect: phishing skirts technology by targeting human beings. That’s why it’s critical to educate employees to recognize and report all manner of phishing attacks.
Gartner argues that the biggest threats are not the ones that risk causing the most damage to you, but simply the vulnerabilities in your organization’s environment that are being actively exploited “in the wild.”
According to its research, the primary method of compromise for most threats is the exploitation of known but unmitigated vulnerabilities, not zero-day threats or new exploits. This is largely a matter of cost: threat actors will continue to primarily use the most cost-effective and reliable exploits instead of new ones because they too have limited time and resources.
Related: Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
How to Address Common Network Security Threats
While each common network security threat has its own individual process for prevention (or elimination), some of the threats are closely related.
For example, organizations typically categorize vulnerability management and patch management in the same sentence. That’s because if you find a vulnerability, you want to patch it immediately, but those are different services.
Similarly, social engineering can cause compromised endpoints. But, your organization should have a way to maintain one and alleviate the other.
Related: Protect Your Business with Cybriant’s IT Security Best Practices Checklist
Common Network Security Threats and Cybriant
- Reducing your threat landscape: We targeted the top 5 common cyber breach vectors mentioned above and bundled services that will reduce your risk of loss due to breach.
- Building a solid security foundation: Our services are based on the NIST Cybersecurity Framework which consists of standards, guidelines, and best practices to manage cybersecurity-related risk.
- Simplify compliance: Each service Cybriant offers will help you operationally comply with any cybersecurity regulatory requirements
- Speeding time to business value: We have the expertise, data, processes, etc. to make your security tools work at peak efficiency. More info at cybriant.com/services
Related: Comprehensive List of All Internet Threats
How to Identify Security Threats to a Network
Keeping track of the security posture of your network is critical in today’s digital age. Networks are constantly vulnerable to malicious actors who use a variety of techniques to infiltrate networks and steal sensitive data. It is essential that you understand how to identify the common security threats that may be present on your network.
The first step in understanding these threats is to understand the type of network traffic that is present in the system. Unusual or unexpected amounts of traffic can indicate a potential security risk. This could be the result of malware, or someone attempting to gain access to your network without authorization. It is important to monitor all traffic and investigate any suspicious activity.
Another way to identify potential risks is by monitoring changes in data or files on your system. Any modification of sensitive data or configuration settings that are not authorized should be investigated further. This can indicate the presence of an intruder attempting to gain access to your system.
Finally, it is important to monitor for unauthorized access attempts. If someone is trying to gain access to your network without authorization, you need to take immediate action to block them from gaining access. It is also important to ensure that all user accounts have strong passwords and follow best practices for security authentication.
Four Types of Network Security Risk
When assessing the security of a network, it is important to understand the four main types of risk. These include malicious software, unauthorized access attempts, data leakage, and changes in the system configuration.
Malicious software such as viruses and malware threaten networks by compromising system integrity or stealing data. Unauthorized access attempts involve someone trying to gain access to the system without authorization. Data leakage occurs when data is unintentionally leaked outside of the network, often through email or unencrypted documents. Finally, changes in system configuration involve someone changing settings or permissions on the system, which can give them access to sensitive information.
It is important to understand these types of risks so that they can be monitored and prevented from impacting your network. By understanding the risks, you can implement strategies to mitigate them and keep your data safe.
One of the most important steps in reducing potential security threats is patch management. Regularly updating software on your system ensures that any critical vulnerabilities have been addressed and reduces the risk of malicious software or unauthorized access attempts. Additionally, it is important to regularly monitor network traffic and verify that the system configuration has not been changed without authorization. This helps to ensure that any data leakage is detected quickly and addressed appropriately.
List of Network Security Risks
- Malicious Software: This type of risk includes viruses, worms, and other malware that can compromise your system integrity or steal sensitive data.
- Unauthorized Access Attempts: This involves someone trying to gain access to the system without authorization.
- Data Leakage: This occurs when sensitive data is unintentionally leaked outside the network.
- Changes in System Configuration: This involves someone changing settings or permissions on the system, which could give them access to sensitive information.
Having a secure network posture is essential for protecting your systems and data from potential threats.