Try a no-risk free trial today!
As I read over the Kroll Global Fraud & Risk Report for 2017, the most common issue discussed is the threat that comes from within your organization. Current and ex-employees were the most frequently cited perpetrators of fraud, cyber, and security incidents over the past 12 months. Notwithstanding this finding, external parties were identified as active perpetrators as well.
In the survey, taken by 545 senior executives worldwide across multiple industries and geographies, 85% said that their company experienced a cyber attack or information theft, loss, or attack in the last 12 months.
The survey also reveals that most cyber incidents involve more than one attack vector. Multiple, interwoven attack
vectors were identified – directly on company software, systems, and websites; via third parties through malfeasance,
attacks on their own systems, or in error; through employee error or malfeasance; and from device theft.
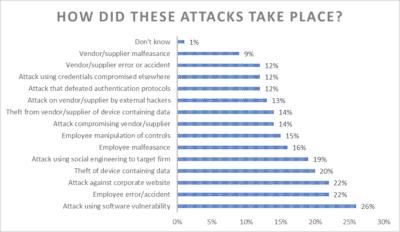
The highest reported attack vector was via software vulnerability, experienced by over a quarter of respondents (26%).
Employee error or accident played a role according to 22% of respondents. And attacks on the corporate website were
noted by 22% of respondents as well.
he findings reveal that threats most commonly come from within. Current and ex-employees were the most frequently
cited perpetrators of fraud, cyber, and security incidents over the past 12 months. Notwithstanding this finding, external
parties were identified as active perpetrators as well.
Nearly 8 out of 10 respondents (79%) cited one of the following categories as the key perpetrator:
Overall, 44% of respondents reported that insiders were the key perpetrators of a cyber incident, citing ex-employees
(20%), freelance/temporary employees (14%), and permanent employees (10%). If we also consider agents/
intermediaries as quasi-employees, noted by 13% of respondents, then the percent indicating that insiders were the
key perpetrators rise to a majority, 57%. Nearly one in three (29%) identified external players as the key perpetrators.
In total, 56% of executives surveyed said insiders were the key perpetrators of security incidents, citing ex-employees
(23%), permanent employees (17%), and temporary/freelance employees (16%).
The good news: 72% have introduced employee cybersecurity training and an equal percentage have employee restrictions on installing software on company devices. Detection methods rank high on the list, with intrusion detection systems, threat intelligence systems, and network operations centers next in magnitude of adoption.
The road to resiliency requires resources, analytics, creativity, understanding of human behavior, and sheer
vigilance to continuously enhance each firm’s ability to prevent, prepare, respond, investigate, and remediate fraud and
risk.
Shoot us a message to start a discussion about how our team can help you today.